Youtube Shorts
Posts
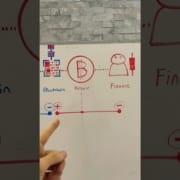
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred.
A principle that perfectly aligns with the ideal operation of money. In this video, we delve into the fascinating parallels between energy and money, and how Bitcoin exemplifies this relationship.
Bitcoin is a unique form of currency produced from energy, but its connection to energy goes deeper than just its production. Each approximately 10-minute update of the Bitcoin blockchain serves as a proof of work, showcasing the immense energy expended by miners worldwide to secure the network and validate transactions.
Bitcoin’s issuance follows a predetermined schedule, with a total cap of 21 million Bitcoins to be mined by the year 2140. After this point, no new Bitcoins will be created, marking the end of its issuance phase. Join us as we explore how Bitcoin’s energy-backed system sets a new precedent for digital currencies and what this means for the future of money
Video Transcript:
the largest two Bitcoin mining pools currently are running over 50% of the Bitcoin Network’s compute power that is the management of a group of compute power to find the next block in the chain on behalf of an entire distributed network of Bitcoin miners around the world now that’s important because the more compute power they get the more Bitcoin blocks that they earn versus other people it’s very very competitive and every small nominal advantage makes the difference and for example you’ve got all of these other smaller pools such pools like Luxor who are introducing products and services within their ecosystem and other things like marapole which is a public minor they don’t let anyone else join their pool but they run their own pool and have extra products and services to accelerate your transactions on top it’s a nent industry that’s very very early and very very Innovative if you think about it
Video Transcript:
does your project use blockchain technology as this magical VC stimulating keyword well the blockchain technology is only best served based on its use cases and that is that for example Bitcoin regulates energy space and time with its blockchain the issuance of money is important so we derive an energy cost to that so you can’t produce a block without consuming energy and when you have money it needs to be traded and transferred all of that information is stored in the blocks and the regulation of how quickly those blocks are arbitrated based on the energy component and regulated Through Time called the difficulty adjustment these different components use blockchain for different things but it all converges into a single circular economy of a monetary system Bitcoin which is distributed fair and demographically sound versus the issuance from a central Authority money is data energy and information all in one what
Video Transcript:
Fun fact for you: did you know that the Bitcoin miners are actually more hardcore DCA buyers than the DCA buyers now DCA buying dollar cost averaging is instead of purchasing your Bitcoin in one lump sum you do it in recurring payments what that does is it removes the volatility of the price from your acquisition now what the Bitcoin miners do is they mine a stack of Bitcoin and they have to sell probably half of it to pay their electricity bill they have to sell something or use something to pay that bill so what you can do is you can use Fiat to pay your electricity bill and then you’re keeping all your Bitcoin which is effectively buying it so if you’ve got that monthly payment of buying your Bitcoin effectively through your electricity bill you have access no fees on exchanging or any liquidity problems of all these exchanges mining gives you direct access to bitcoin from the source so you’re a more hardcore DCA than the DCA […].
Video Transcript:
Crazy fact for you did you know that Bitcoin miners aren’t actually producing their own Bitcoin instead they sell their raw material compute power hash rate to a mining pool who manages an entire pool of hash rate to mine blocks faster and the reason for this is if you’re a tiny tiny percentage of the network you’re going to get a tiny tiny percentage of the blocks and if the blocks are only 144 per day well then to get one block a day you need to be 144th of the network which is actually tens of millions of dollars worth of Hardware if you’ve only got a small amount it means that you may find a block every 3 months but what if your electricity bill is monthly you have an imbalance of cash flows so people join mining pools sell their hash rate are paid Bitcoin in return and the poll manages the production of Bitcoin blocks […].
Video Transcript
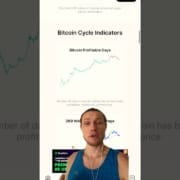
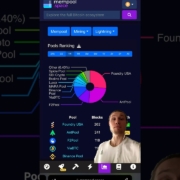
so the Haring has occurred and as you can see miners Revenue per Peta has per day got cut in half but the Haring actually caused a spike in income for miners because of fees now what happened was the launch of a new protocol called runes which is a different way of storing different data in Bitcoin blocks because remember your transaction fee and the size of your transaction fee in Bitcoin is based on the data size how much data you’re putting on the blockchain instead of the size of the amount of Bitcoin you want to send it’s there’s no difference as to the size it’s all based on how much data you’re paying to store in the blocks now why is this important well because in the future of Bitcoin mining we’re going to see more dependence on transaction fees which are volatile than the subsidy which is guaranteed every single block this creates a more volatile fee environment as shown below

















Social Media